RFP evaluation criteria are the scorecard for decision-making. They help buyers cut through the noise, measure proposals fairly, and select the best-fit vendor. For responders, the hidden playbook shows exactly how your proposal will be judged.
But as RFPs evolve, so do the evaluation models. Buying committees are bigger. Timelines are tighter. More organizations are using AI to both issue and score RFPs. In this guide, we’ll cover the essentials of RFP evaluation criteria, show examples, and share practical tips for both issuers and responders.
What are RFP evaluation criteria?
Request for proposal (RFP) evaluation criteria is a set of standards that guide the scoring of vendor proposals. When put into practice, your RFP evaluation criteria standardize scoring and remove subjectivity from the process. Proposal issuers use criteria to organize the proposal evaluation process and select the right vendor for their procurement projects.
Generally, both internal and external teams receive the RFP evaluation criteria. Specifically, vendors review scoring criteria as a part of the RFP documentation. And, your internal stakeholders who will participate in RFP scoring will use it as a reference document.
In addition to improving confidence in vendor selection, clear evaluation criteria set expectations, ensure high-quality RFP responses, and deliver fairness and transparency to the process. Indeed, scoring guidelines help vendors focus on the issues and areas of the RFP that are most important to you.
Common RFP evaluation criteria
Below, we’ve outlined some of the standard criteria teams will use when evaluating an RFP; however, this is certainly not an exhaustive list.
- Cost and value: Pricing is always a factor, but lowest cost rarely wins. Buyers want clear ROI and long-term value.
- Capabilities: Core product or service functionality that meets defined requirements.
- Scalability and innovation: Vendors who can grow with the business and bring fresh ideas often earn extra credit.
- Security and compliance: Critical in regulated industries like financial services.
- Customer experience: Training, onboarding, and support often make the difference in adoption.
- Cultural fit: Buyers increasingly want partners who align with their mission and ways of working.
Why are evaluation criteria important?
The buying process is more complex than ever. According to Responsive’s 2025 State of SRM Report, more than 75% of organizations reported that buyers expect faster, more personalized responses, while also involving more stakeholders.
Clear evaluation criteria help in three significant ways:
- Fairness and transparency: Everyone knows the rules upfront, which builds trust with vendors and confidence among stakeholders.
- Efficiency: With a scoring model in place, committees can move faster and cut through debates that stall decision-making.
- Risk management: Structured evaluation ensures compliance and reduces the chance of overlooking critical requirements.
When done well, evaluation criteria help teams move faster and make informed decisions. Done poorly, they leave room for bias, delays, and costly missteps.
Ways to organize your RFP evaluation criteria
The evaluation criteria will vary depending on the project. You can create a standard RFP evaluation scoring guide, but you will need to use it as a template and update it for each project.
Simple evaluation criteria
The most straightforward approach to RFP evaluation criteria is a simple list. If your RFP project is a low-risk, simple purchase, you may not need to develop a complicated scoring system.
In this case, note your highest-priority factors, along with minor considerations, in the introduction and background section of your RFP. Then, when you’re ready to score the proposals, remind your evaluators of the stated criteria. Finally, verify your results by comparing your selected supplier’s responses to the requirements.
RFP evaluation criteria matrix
An RFP evaluation criteria matrix is a popular method, as it can be created in a spreadsheet and tailored to be as simple or complex as needed.
For example, a simple matrix lists criteria on the left-hand side with the potential vendors along the top, allowing scorers to evaluate and compare options broadly.
On the other hand, a detailed matrix breaks down scoring to the question level. This enables you to focus on detailed components and nuanced responses. Typically, strategic sourcing projects use detailed evaluation criteria matrices.
RFP weighted scoring
The weighted scoring approach breaks down your RFP evaluation criteria and assigns a value to each question or section. For example, your RFP criteria may consider questions of technical expertise, capabilities, data security, HR policies, and diversity and sustainability. Weighted scoring prioritizes the requirements most important to your business by assigning them point or percentage values.
So your weighted scoring criteria may look like this:
- Technical expertise – 25%
- Capabilities – 40%
- Data security – 10%
- HR policies – 10%
- Diversity and sustainability – 15%
A note about RFP evaluation:
Managing RFP scoring in spreadsheets gets messy quickly. When it comes to complex strategic sourcing projects involving more than three vendors, manual evaluation is time-consuming, thereby increasing procurement costs.
For many procurement teams, RFP software provides a solution. An RFP management system delivers efficiency with digital proposal responses, RFP automation, and collaborative scoring.
Examples of RFP evaluation criteria
Without seeing the evaluation process in action, the RFP evaluation criteria can be hard to picture. So, the best way to understand it is to see it in practice.
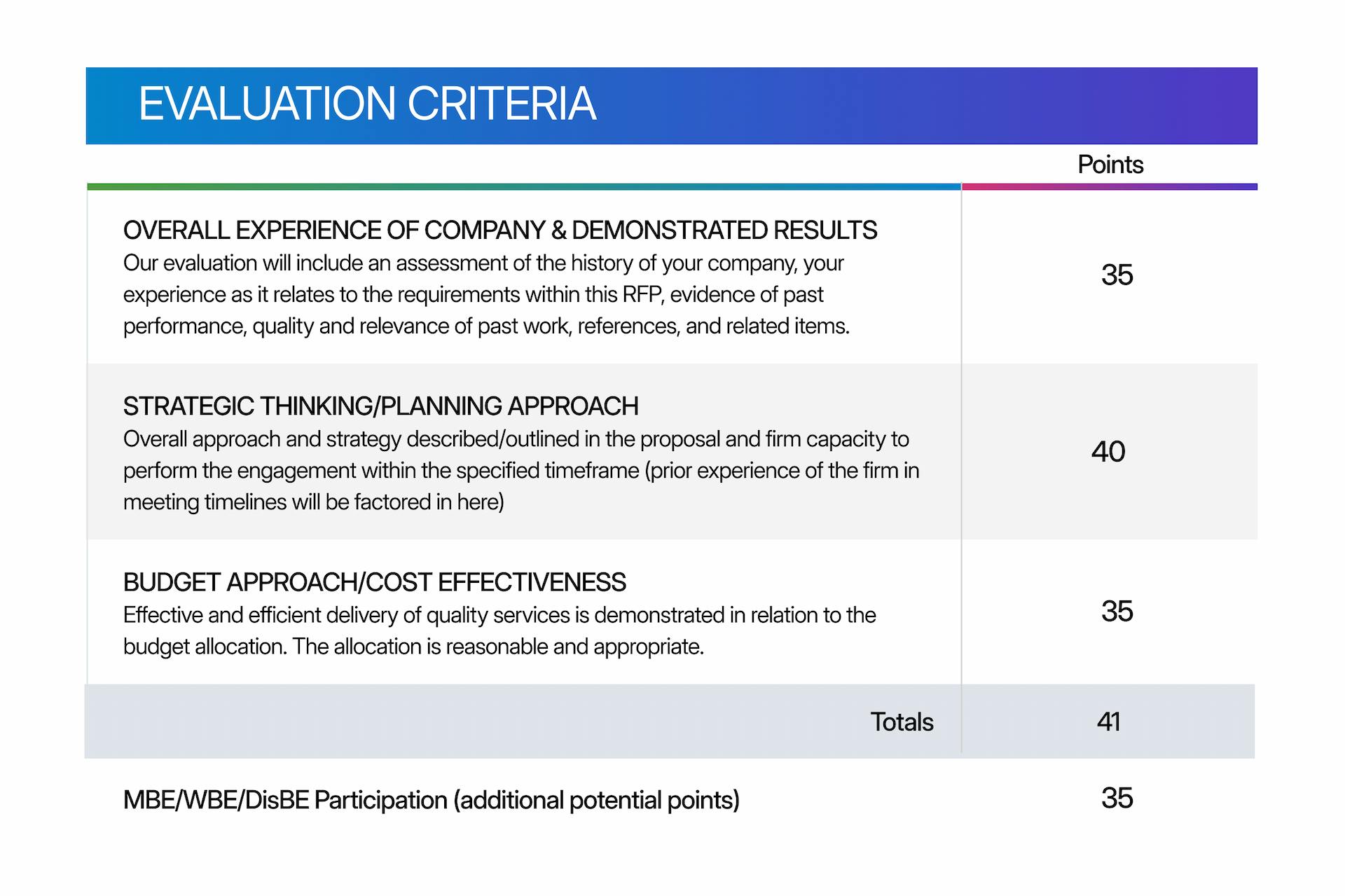
Basic weighted scoring criteria
In this RFP for employee benefits example, results are broken down into three main categories: experience, approach, and budget. The point totals are both weighted and relatively simple.
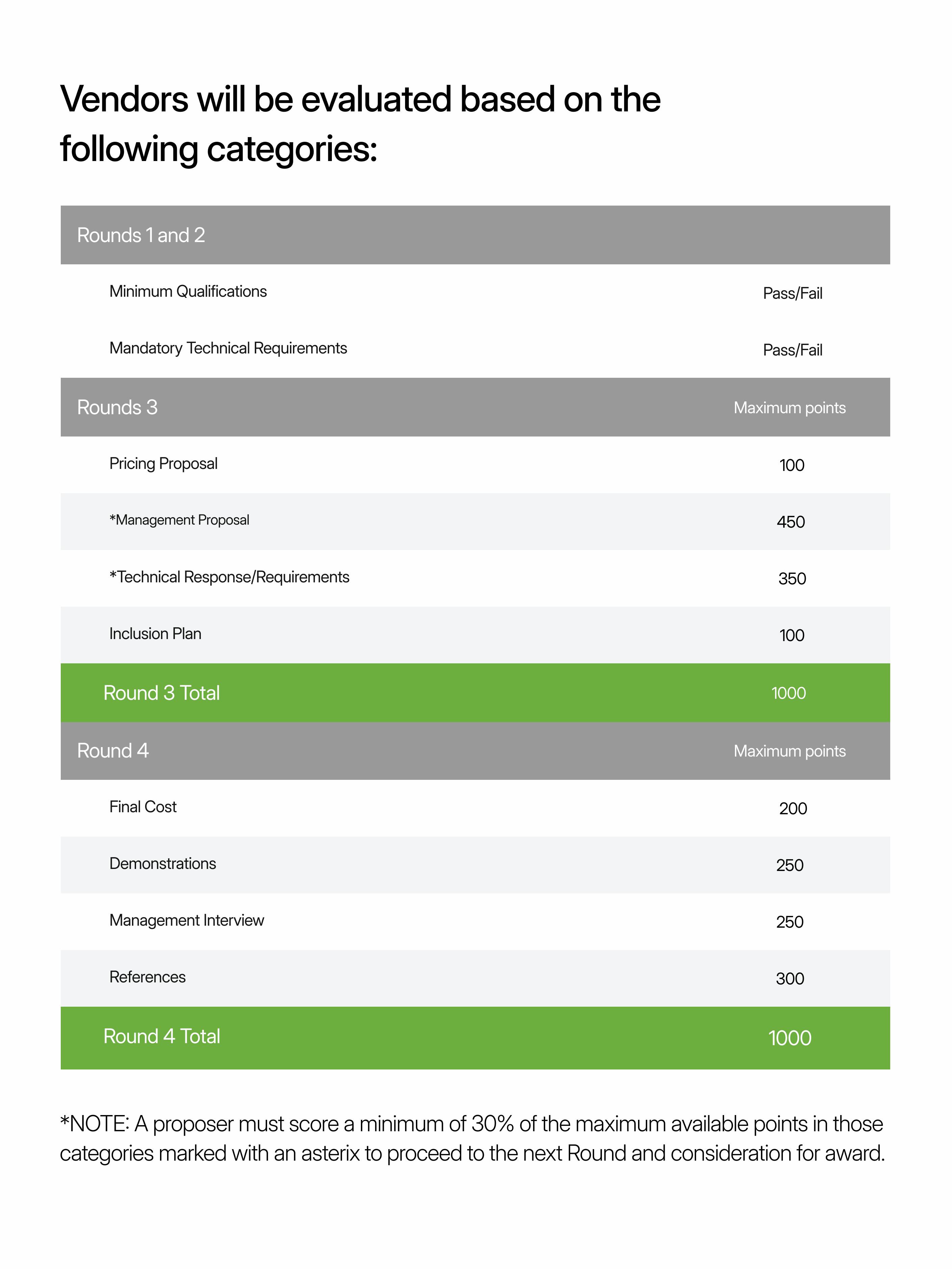
Multi-factor RFP evaluation criteria
In this RFP example for a data analytics platform, the evaluation is broken down into four rounds. Interestingly, the first two are pass/fail criteria that are deal breakers. This staggered evaluation helps vendors quickly understand if they will be eligible to win the business.
How to write RFP evaluation criteria
1. Gather requirements with stakeholders
Start by meeting with stakeholders to capture their needs and expectations. Provide a starter list of common evaluation areas—such as technical capabilities, vendor experience, project approach, customer support, data security, and pricing—and encourage open brainstorming. Look for recurring themes, as those often point to the highest priorities.
2. Define scope and deal-breakers
Once you have the complete list, sort it into must-haves, nice-to-haves, and not-needed items. Convert must-haves into clear, closed-ended questions in your RFP so evaluators can quickly determine whether a vendor qualifies. Keep track of any deal-breakers as you build the questionnaire.
3. Set priorities and weightings
Not all criteria carry the same weight. Decide which areas matter most—often functionality, security, and vendor expertise outweigh cost—and assign values accordingly. Clear priorities make it easier for evaluation teams to score proposals consistently and select the best partner.
Best practices for RFP evaluation criteria
Be transparent
The more vendors know about your priorities, the stronger their proposals will be. Share your evaluation criteria (and weightings) upfront. It builds trust and ensures you get responses that address what matters most.
Stick to your criteria
Once you’ve set evaluation rules, follow them without deviations. If a new requirement arises, notify all vendors so they can respond in a timely manner. Transparency keeps the process compliant and avoids bias.
Create an evaluation guide
Provide evaluators with a simple playbook that explains the scoring model, criteria, and priorities. Clear guidance reduces confusion and makes scoring more consistent across stakeholders. Here are two examples of internal documentation for RFP evaluators:
Involve the right people
Invite input from those who will actually use the solution. Individual scoring works best, since group sessions often skew toward the loudest voices. Tools like the Responsive Platform make it easy to assign questions and gather scores without slowing things down.
Keep contributors focused
Only share the sections each stakeholder needs to evaluate. For example, HR scores usability, while IT reviews security. Assigning tasks by expertise helps avoid bottlenecks and keeps the process moving smoothly.
Address scoring discrepancies
Different perspectives are natural. If evaluator scores vary widely, talk it through. Misalignment often indicates unclear questions or misunderstood requirements. These are issues worth addressing before final selection.
The future of RFP evaluation criteria
Evaluation criteria have shifted as AI has and continues to reshape the buying and selling process. Buyers are now using AI to issue RFPs and analyze responses. Vendors are utilizing SRM tools to manage knowledge, generate content, and ensure compliance, thereby better positioning themselves to stand out.
However, the fundamentals remain the same: fairness, clarity, and consistency. The winners will be those who use evaluation criteria not just to check boxes, but to tell a story of partnership, growth, and trust.
